
SS-VMI
Surface Scattering Velocity Map Imaging
We describe an adaptation of the velocity map imaging (VMI) technique: surface scattering velocity map imaging (SS-VMI), which allows you to measure the full 2D scattering plane of a gas-surface process. The initial implimentation of our SS-VMI technique was reported in the Review of Scientific Instruments here.
Experimental Layout
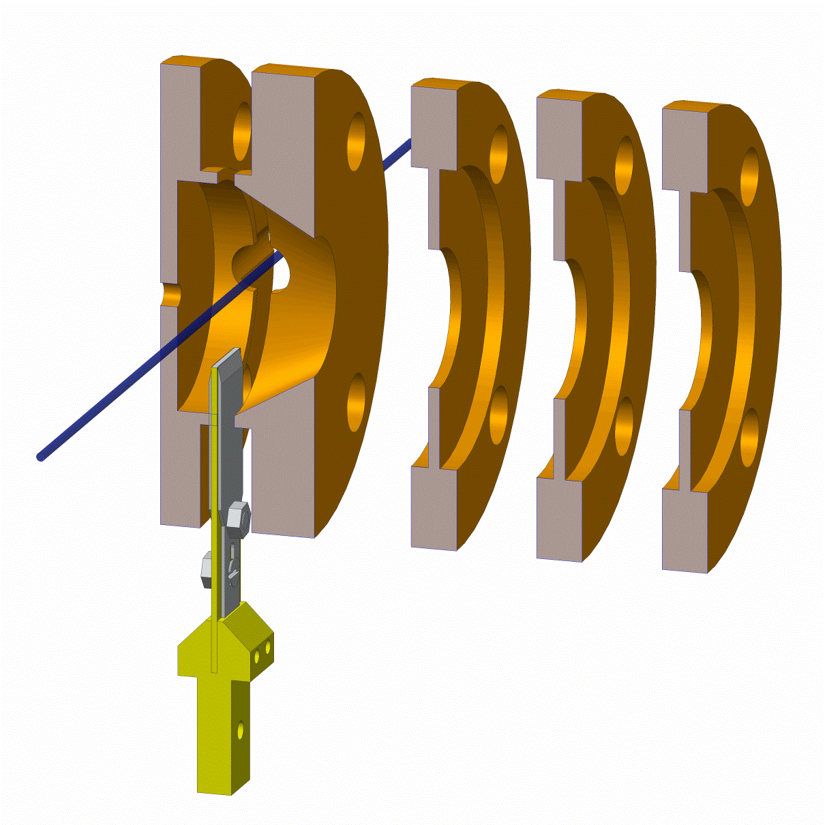
The figure below shows a cut through the ion optics which reveals the surface holder with stabilising electrodes and the path of the product ionization laser.
Initial experiments to demonstrate the quality of the velocity mapping with an electrically stabilised surface within the electric fields compared images of the photodissociation of CD3I with and without the surface present (Fig. 2 in the publication). However these images were taken with the molecular beam carrying the CD3I travelling parallel to the imaging detector. As such these images were blurred in the vertical direction by the spread in molecular beam speeds and the spread of internal energies taken by the CD3 fragment. By moving the molecular beam axis to be perpendicular to the detector (as is typical in a photodissociation VMI experiment), and by changing the molecule to be photodissociated we can demonstrate the power of the SS-VMI technique. The figure below shows the comparison of two NO2 images, taken with the surface present in the ion-imaging electric field (SS-VMI), and without the surface present (VMI).

The SS-VMI image was taken with the surface to laser distance set to 10 mm, and shows the excellent performance of the SS-VMI set-up.
SS-VMI Development
Future developments to this experiment will involve the following strands:
- Improving the design of the ion optics through SIMION simulation
- Refining the stabilising electrode design
- Development of devices to enable a flowing liquid surface to be used
The last strand has been developed this year by an MChem project student, Andrew Burton, who has developed a prototype in vacuum liquid flow device (design pictured below).
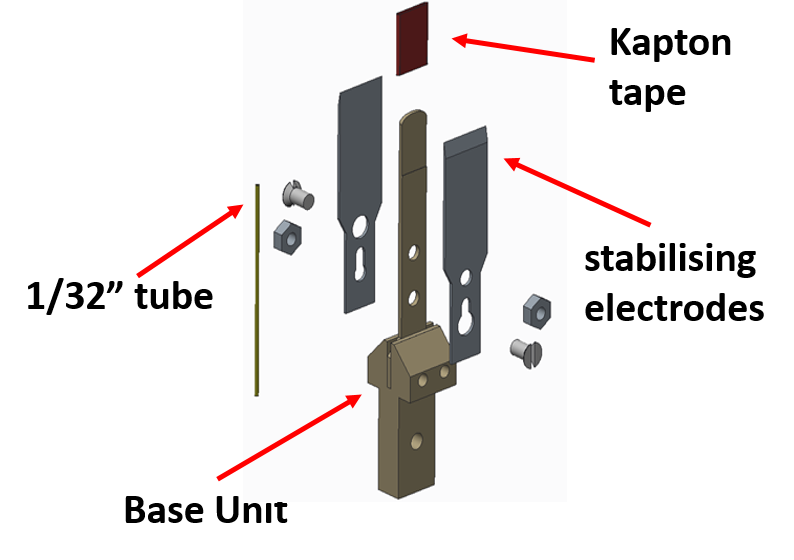
-
Note: Velocity map imaging the scattering plane of gas surface collisions
Rev. Sci. Instrum. 87 106104 (2016)
doi: 10.1063/1.4965970

Go to top